Toyota Is Right: We Need More Hybrid Cars and Fewer EVs.
Story by James Gilboy 11/02/2023
The Case for Hybrids Over EVs
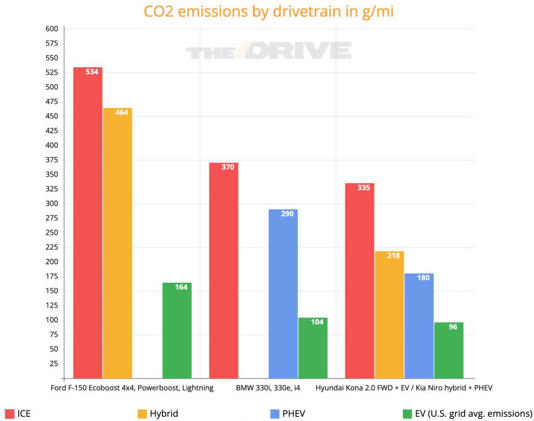
To illustrate, we’re going to compare the on-road carbon emissions of a few models that are available with internal combustion, hybrid/PHEV, and electric powertrains: the Ford F-150, the 2022 Hyundai Kona and Kia Niro (which use the same chassis) and the BMW 3 Series and i4 (which also share their bones). Again, this is the question we want to answer: What’s the best use of a limited battery supply? Do we spread those materials across a bunch of hybrids, or cram them into a few EVs and leave the remainder with straight gas or diesel engines?
We can answer this by dividing how much each vehicle reduces CO2 emissions over its ICE counterpart by its battery capacity in kilowatt-hours. That’s tricky to imagine, so don’t bother: just look at this equation instead.
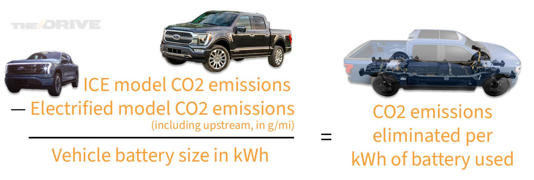
Toyota Is Right: We Need More Hybrid Cars and Fewer EVs. Here’s Why© Provided by The Drive
Calculating battery use efficiency in electrified vehicles. The Drive
We need more data to fill that out, of course, and obtaining it is simple: The EPA’s FuelEconomy.gov publishes per-mile CO2 estimates, which also estimate the upstream emissions that come from gasoline production.
Things aren’t as straightforward for EVs, though, which the EPA lists as emitting no CO2. While true from an exhaust standpoint, making the electricity needed to charge them does generate CO2: an average of 386 grams of it per kWh in the United States, according to the Energy Information Administration. We can then estimate their hidden CO2 emissions with the equation illustrated below. (It’s the same formula we used to calculate the break-even point for EVs when it comes to charging and production emissions vs their on-road savings last year.)

Toyota Is Right: We Need More Hybrid Cars and Fewer EVs. Here’s Why© Provided by The Drive
Calculating the hidden emissions of EVs. The Drive
Armed with this data, we can then calculate how efficiently each electrified vehicle uses its battery. The equation we’ll use for that is shown above—remember, the goal is to reduce CO2 emissions as much as possible with a limited supply of batteries. And when you do the math, it’s pretty clear what the best option is.
Made with LiveGap Charts
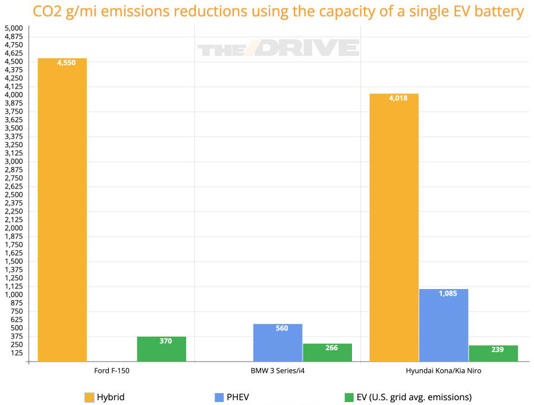
Consider just how much battery your typical mass-market EV uses. Operating an F-150 Lightning may generate less than a third of the CO2 emissions of a gas F-150, but each one hoards 98 kWh of battery, most of which will be used only on the rare prolonged drive. Meanwhile, an F-150 Powerboost hybrid battery is just 1.5 kWh. It doesn’t achieve nearly the emissions reduction the Lightning does, but Ford could make 65 of them with the batteries that go into a single Lightning.
Toyota Is Right: We Need More Hybrid Cars and Fewer EVs. Here’s Why© Provided by The Drive
That adds up, because if Ford sells one Lightning and 64 ICE F-150s, it’s cutting the on-road CO2 emissions of those trucks as a group by 370 g/mi. If it sold 65 hybrids—spreading the one Lightning’s battery supply across them all—it’d reduce aggregate emissions by 4,550 g/mi. Remember, this is using the exact same amount of batteries; the distribution is just different.
Toyota Is Right: We Need More Hybrid Cars and Fewer EVs. Here’s Why© Provided by The Drive
The pattern holds true for the Hyundai/Kia combo and the BMWs, too—going full hybrid lowers emissions far more than building a handful of EV and a ton of gas cars. Split up an i4’s battery, and you can make seven 330e PHEVs, cutting 560 g/mi to one i4’s 266. Divvy up a Kona EV’s, and you can make seven Niro PHEVs worth 1,085 g/mi in reductions (one EV’s worth 239), or 41 regular Niro hybrids, for 4,797 g/mi eliminated. Like the Ford, they make better use of a fixed battery supply by spreading it across a large number of hybrids, rather than concentrating them all in a single EV.
Toyota Is Right: We Need More Hybrid Cars and Fewer EVs. Here’s Why© Provided by The Drive
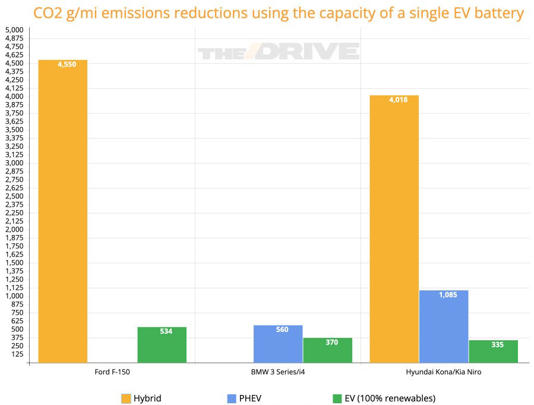
Of course, EVs’ cases improve when they’re run exclusively on renewable energy. We can zero their per-mile CO2 emissions to simulate that, and it helps them out—but it doesn’t change the fact that their battery use is still inefficient. Powering a handful of EVs with renewables still just doesn’t have the immediate effect that a broader hybridization of new cars would.
It comes down to this: By using its limited battery supply on a small number of (expensive) EVs, the auto industry gets plaudits from investors and the public despite implementing an inefficient decarbonization scheme. It gets to greenwash itself with a handful of flashy products, while in fact not cutting CO2 emissions nearly as much as it could. The numbers strongly suggest that hybridizing as many new cars as possible is more effective, and to increasing degrees as battery technology evolves and supplies hopefully go up. That would allow hybrids to graduate to PHEVs, before being superseded by full EVs where appropriate.

Toyota Is Right: We Need More Hybrid Cars and Fewer EVs. Here’s Why© Toyota
Most of the benefits of a full EV transition, however, would present themselves with widespread PHEV adoption. They offer enough range to make short trips on electric power alone, often at comparable up-front cost to an EV, but also the flexibility and efficiency of a hybrid powertrain for longer journeys. This lets them sidestep most of the obstacles to EV adoption, namely battery supply and poor charging infrastructure.
That said, there are reasons why PHEVs haven’t taken off. They’re less efficient and more complicated to produce and service than EVs or regular hybrids, not to mention heavier and more expensive than regular hybrids. They’re also not helped by their confusing names, never mind the PHEV acronym.
2023 Toyota Prius. Peter Nelson
Hybrids as a whole have taken a long time to capture market share, accounting for just 5.5 percent of the light vehicle market in 2021, according to the Bureau of Transportation Statistics. That’s over a period of 24 years since the pioneering Toyota Prius entered production. EVs meanwhile achieved a similar market share in less than half that time, attaining 5.8 percent of the U.S. market in 2022 according to The Wall Street Journal. That’s only a decade since the paradigm-shifting Tesla Model S entered production.
But EV buyers benefited from more generous tax incentives than hybrid customers ever did, with the previous federal EV tax credit effectively conjuring the market out of thin air. Like it dictates the sizes and kinds of cars we buy, both directly via the Chicken Tax and indirectly a la CAFE regulations, government policy strongly influences which powertrains we choose.
So far, the government has favored the shiny, hype-driven solution of fast-tracking EV adoption, when the math suggests that’s suboptimal—at least for the short and medium term. If anything, it’s probably fair to say the over-emphasis on EVs is slowing the decarbonization of the auto industry for the time being. We can’t afford to overlook the role hybrids have to play here and now in favor of a far-flung future where every car on the road is pure electric.
Besides, when the 2023 Toyota Prius is one of the best-looking cars on sale today, it makes the pragmatic solution that much easier to choose.
Toyota Is Right: We Need More Hybrid Cars and Fewer EVs. Here’s Why (msn.com)








